The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued a new regulation for Methylene Chloride or Dichloromethane (DCM) Under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) in May 2024. Under this new regulation, the EPA is banning almost all industrial, commercial, and consumer uses of DCM (CAS # 75-09-2). There are now many new restrictions and conditions on the continued use of methylene chloride. As part of the regulations, EPA requires exposure monitoring for all uses of DCM on campus.
Risk Management and Environmental Health & Safety (RMEHS) is reaching out to departments that list DCM in their chemical inventory to confirm the need for continued use of the chemical. If continued use is required, RMEHS will need to conduct exposure monitoring in most workshops/laboratories and will assist users with other compliance requirements that are mandated by the EPA. To help RMEHS coordinate your compliance with this new regulation, it is critical to keep your chemical inventory up to date.
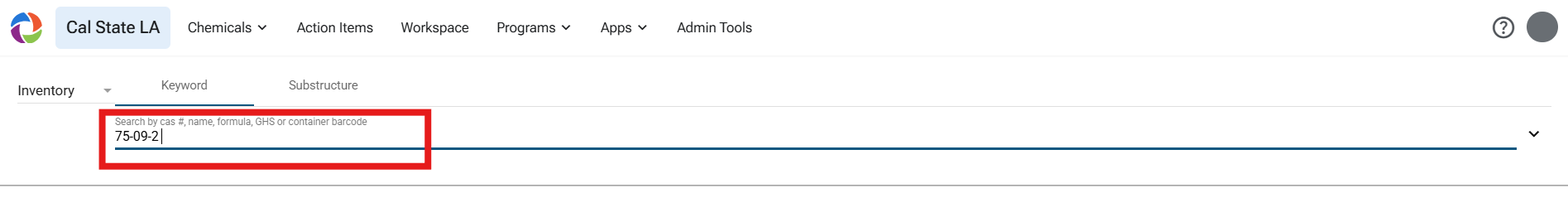
NOTE: THESE RULES APPLY TO DCM AND DCM-CONTAINING PRODUCTS. ENSURE YOU SEARCH YOUR INVENTORY USING THE CAS NUMBER.
Common Questions About the DCM Regulation
Below are answers to the most common questions about this new regulation, If you have additional questions or concerns, please reach out to RMEHS at [email protected] or ext. 3-3531 for additional guidance.
DCM-containing products refer to household or commercial products that contain DCM or have a percentage of DCM in their ingredients. Below is a common list of items that are known to contain DCM. this list is not all inclusive and specific items in your inventory should be check for DCM.
Note: In advance of the 2019 EPA ruling, many retailers phased out methylene chloride or dichloromethane-containing products. These include Walmart, Lowe’s, Home Depot, Sherwin Williams, and Ace Hardware, all by late 2018 or early 2019.
- Varnish remover
- Masonry cleaner
- Graffiti remover
- Paint stripper
- Surface preparation cleaner for painting/gluing
- Adhesive, tape, or tacky remover
- Degreaser / Parts stripper (commonly for metal parts)
- Epoxy dissolver
- Soldering rosin flux remover
- Paint brush cleaner (note this does not include simple mineral spirits nor pure paint thinner, but does include brush deep cleaning solvents or brush restoring cleaners for dried paint)
- Foam dissolver
- Caulk/sealant remover
- Laminate stripper
- Tile remover
- Bathtub refinisher
- Carburetor cleaner
- Choke and valve cleaner
- Brake cleaner (automotive)
- Gasket remover
- Gun/firearm cleaner
- Spray equipment cleaner
- 3-D printer nozzle cleaner
- Contact cement – particularly older spray contact cement (manufacturers or brand names in particular include Hybond, Tensorgrip, Formica, Weld-on; possibly older 3M products) (Note that Wilson Art Company makes a non-flammable alternative contact cement with no DCM is present as of 2024).
- Wallpaper and/or carpet glue remover
- Mold-release agents (McLube is one possible name brand)
- Various name brands of all the above products, whose products presently or in the past have contained DCM (especially in strippers/cleaners), include Sterling, Watco, Jasco, Klean-strip, Savogran, Miller-Stephenson, and Zinsser.
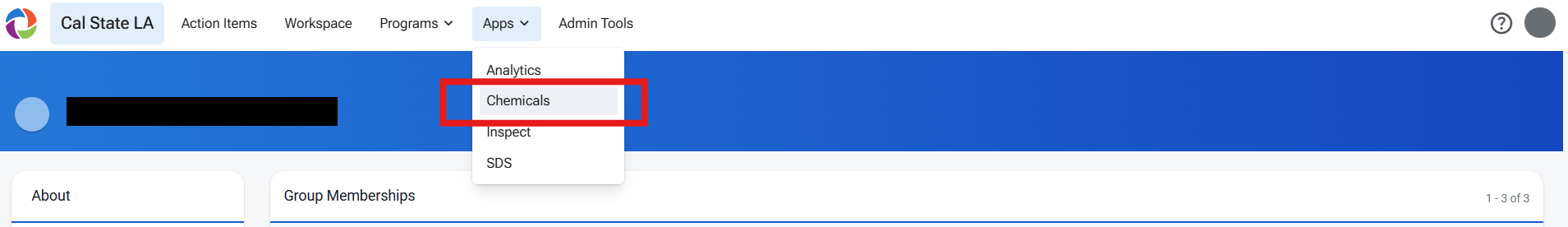
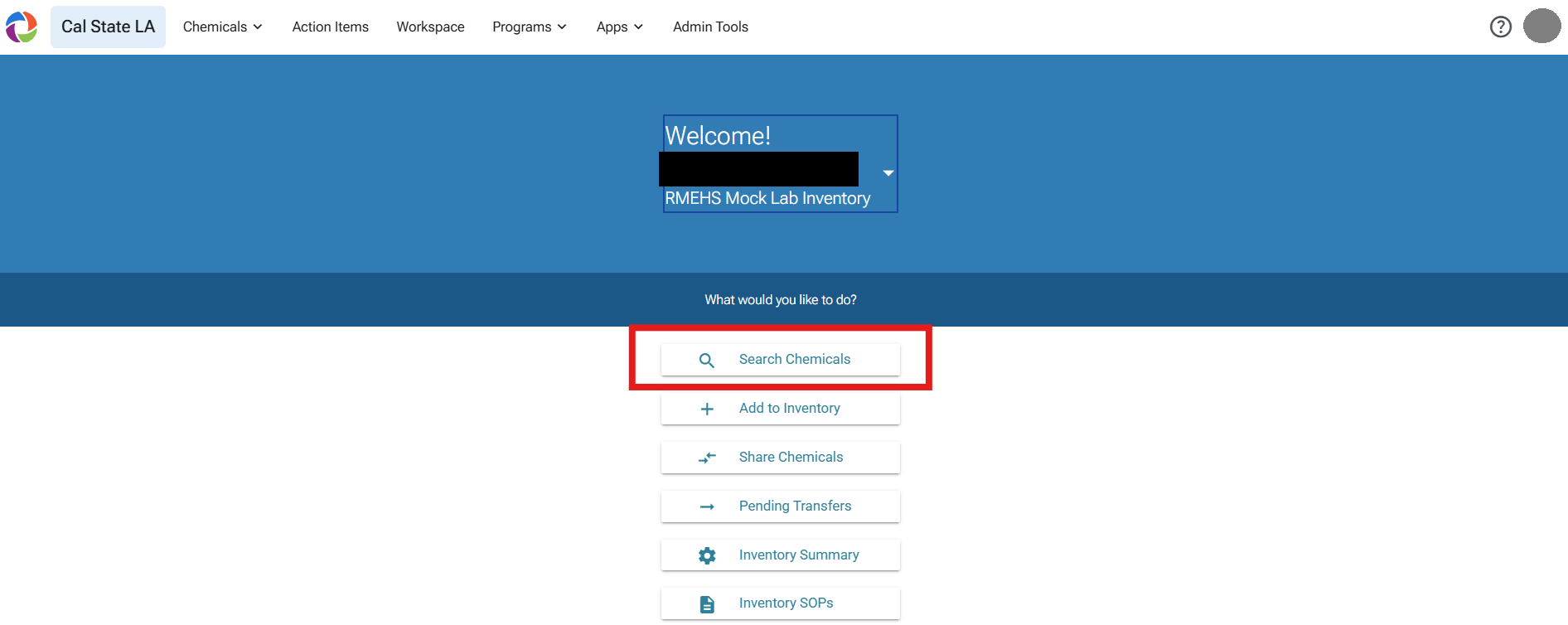
Note: The search feature in Risk and Safety Solutions (RSS) can provide a list of DCM and DCM-containing chemicals if your inventory is maintained and updated.
Please follow the instructions below to determine if DCM or DCM-containing products are in your inventory
The EPA determined that DCM presents an unreasonable risk to human health. DCM is classified as a potential human carcinogen and is toxic to the central nervous system and the liver. Exposure to DCM can occur from inhalation and skin absorption.
At least 85 deaths have resulted from exposures to high levels of DCM, primarily during paint-stripping and bathtub refinishing activities in poorly ventilated areas.
If you would like to dispose of any unused DCM or no longer wish to use DCM, please submit an RMEHS Service Request platform and select 'Waste Disposal Services' after submitting general information for contacting purposes.
You can also participate in the 2025 Chemical Cleanout Event for large quantities and disposal of other hazardous materials.
Once the proper disposal has occurred, please remove any chemical containers from your inventory to ensure proper reporting has taken place. For instructions on managing chemical inventories within the RSS platform, refer to the RSS Help and Guidance webpage for detailed information on the RSS Chemical Inventory process. Additionally, the RSS Academy Trainings provide live learning sessions and instructional videos for further guidance.
This regulation applies to all research, government, academic, industrial, and commercial laboratories or workshop spaces that use and store DCM in their area. Additionally, this regulation applies to all potentially exposed laboratory/workshop personnel, including faculty, staff, students, interns, and visitors.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) requires employers to implement a Workplace Chemical Protection Program (WCPP) to protect laboratory personnel from exposure to DCM. Under the WCPP, we are required to:
- Meet the exposure limits for methylene chloride established by the EPA. The EPA exposure limits are lower than the exposure limits established by Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA).
- Conduct initial and periodic exposure monitoring for all potential methylene chloride exposures.
- Establish a regulated area when airborne concentrations of DCM exceed, or there is a reasonable possibility they may exceed the exposure limits and mark those areas accordingly.
- Develop and implement a DCM exposure control plan that identifies the controls used to reduce exposures to below the exposure limits.
- Record keeping requirements for RMEHS.
- Provide appropriate respiratory selection and other PPE for individuals that may enter the regulated areas.
- Conduct training for all individuals that will enter the areas where DCM is used.
As mentioned previously, exposure to DCM can occur from inhalation and skin absorption. It is important that control measures are in place to prevent both inhalation and skin contact. Methods for controlling DCM exposure are listed below in order of most effective to least effective:
Elimination or Substitution
If possible, eliminate the use of DCM or replace DCM with a safer alternative. If you are able to eliminate the use of DCM in your lab, submit a RMEHS Service Request platform and select 'Waste Disposal Services' after submitting general information for contacting purposes, for pickup.
Engineering Controls
When elimination or substitution is not feasible, engineering controls are the next most effective control method. Chemical fume hoods are the most common engineering control found in laboratories. Work with DCM in a fume hood whenever possible. If a fume hood is not available or is not able to be used for a specific application, contact RMEHS to assist with identifying appropriate alternative controls.
Administrative Controls
Implement work practices that reduce the quantity of DCM used, the duration of exposure, and/or the frequency of use if possible. The required establishment of a regulated area is an example of an administrative control.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Unfortunately, PPE for DCM is not straightforward. Many common glove materials do not provide protection from DCM, including nitrile, latex, neoprene, and butyl rubber. DCM permeates disposable nitrile gloves within one minute. If you have the potential for hand contact with DCM, one solution that will provide good protection and dexterity is to double glove with Silver Shield® gloves as the inner gloves and disposable nitrile gloves as the outer gloves. Contact RMEHS for additional glove selection assistance.
Using air-purifying respirators (APRs) as respiratory protection is not an option for controlling inhalation exposures to DCM in the lab or workshop space.
Please note that filter cartridge respirators cannot be used because DCM can pass through the cartridge leaving respirator wearers unprotected. Breakthrough of APR cartridges offers no indication before the odor threshold, by which overexposure will have occurred.
Substitutes for DCM may be available depending on your application. RMEHS discussed many of these options in the Town Hall hosted in December 2024 and is available for your convenience.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) has several tools available for identifying substitutes on their Tools for Innovation in Chemistry page. Additionally the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has a list of common substitutes for general applications listed below.
- D-Limonene,
- Propylene Carbonate, or
- Acetone
Please be aware that some substitutes may introduce different hazards, such as flammability. The Chemical Hygiene Officer of RMEHS is available to consult with you to help identify substitutes and to ensure any new hazards are identified and properly controlled.
Exposure monitoring measures a person's exposure to airborne chemicals during use. There are several different methods for conducting exposure monitoring, and the method selected will be based on the specific use scenario.
Certified Industrial Hygienists are required to perform exposure monitoring for your laboratory/ workspace where needed. Each PI/department responsible for a regulated DCM space is required to hire a certified industrial hygienist to measure exposure for both the initial and periodic monitoring when DCM is in use.
Yes, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has stated that while a properly working fume hood should be sufficient to control methylene chloride exposures, exposure monitoring is needed to demonstrate the protection provided.
Yes. DCM waste will continue to be disposed of adhering to the existing rules for hazardous chemical waste disposal. The primary difference between this and other upcoming EPA regulations is that users should not fill or pour chlorinated organic waste in the open laboratory or workshop but rather only under ventilation (such as in a fume hood).
Halogenated/chlorinated waste containers must be kept capped at all times when stored outside of ventilated space. These apply unless and/or until exposure monitoring determines whether overexposure may occur with these activities.
To assist us with complying with these new regulations:
- Ensure your chemical inventory is up to date in Risk Safety Solutions (RSS).
- Identify old and unused containers of DCM in your lab and submit an RMEHS Service Request by selecting 'Waste Disposal Services.'
- Sign up for the annual Chemical Cleanout Event (for large quantities and disposal of other chemical containers)
- Register by April 18, 2025
- Assessment by May 1, 2025
For instructions on managing chemical inventories within the RSS platform, refer to the RSS Help and Guidance webpage for detailed information on the RSS Chemical Inventory process. Additionally, the RSS Academy Trainings provide live learning sessions and instructional videos for further guidance.