Robert M. Nissen Lab Research
Wdr68 is required for craniofacial development
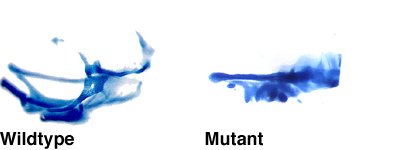
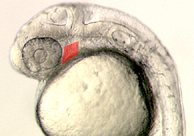
The maxilla is the upper jaw and the mandible is the lower jaw. The adult jaws form over an embryonic cartilage scaffold. These embryonic cartilages can be seen in 4 day old zebrafish larva stained with Alcian blue.
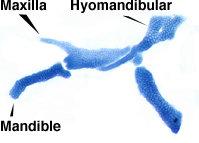
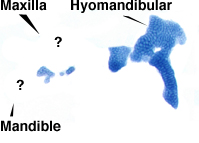
The seemingly complex embryonic cartilages are actually quite simple when viewed after flat mounting (at left). In zebrafish embryos, the ptergoid process (PTP) of the palatoquadrate (PQ) cartilage serves as the embryonic maxillary region and the Meckel's cartilage (MC) serves as the embryonic mandible region. The hyomandibular (HM) region anchors the jaws to the skull. The second image displays the flat mounted jaw of the wdr68 mutant which shows severe reductions of MC and PTP/PQ regions.
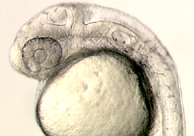
The MC and PTP/PQ cartilages are derived from neural crest (NC) cells that occupy the first pharyngeal arch. The second image displays a 28 hours post-fertilization (hpf) embryo at left to highlight the first arch region. Within the first arch, subsets of the NC cells receive signals that instruct them to form the various cartilage elements, including MC, PTP, PQ. The endothelin-1 (edn1) signaling pathway is essential for MC formation. The genes required for PTP/PQ formation are less well understood.
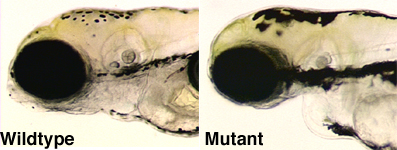
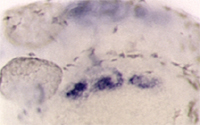

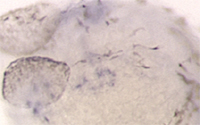
The wdr68 gene is insertionally disrupted in wdr68 mutants indicating that the wdr68 gene is essential for both MC and PQ formation. We demonstrated that wdr68 is required for edn1 expression explaining the severe reduction in the MC region. At left is an in situ hybridization to detect edn1 expression on 28hpf wildtype and mutant animals (the second image shows the mutant view). Currently, we seek to understand how wdr68 promotes edn1 expression and to define the wdr68-dependent gene networks that are required for PTP/PQ formation.